
As more and more businesses and industries are digitizing, they’re generating tons of raw data. Analyzing and managing that data is key to making more informed, data-driven decisions, improving customer satisfaction, and running successful campaigns.
Business intelligence (BI) is the strategies and technologies used to convert all that raw data into usable information. Depending on your business needs, you can use BI tools to improve efficiency and performance, or even sell the data to other companies.
We’ve collected 13 useful and surprising business intelligence statistics that will give you a competitive advantage.
Let’s get right into it.
1. The business intelligence market size is $25.73 billion in 2023 (Source)
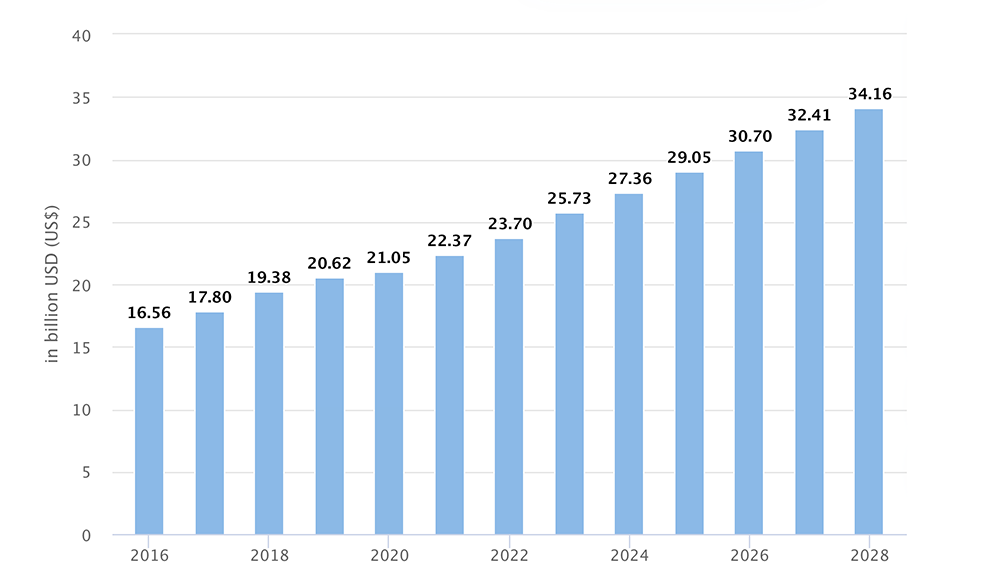
With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.83%, the BI market size is expected to reach $34.16 billion by 2028.
Furthermore, Statista Market Insights projected that the average spend per employee in the BI software market will be $7.39 by the end of 2023, and that the United States will generate the most revenue in the BI industry that year at $13.15 billion.
In the past few years, the business intelligence industry saw its lowest revenue change in 2020 at 2.9%. This was a drop from 6.4% in 2019 and 8.88% in 2018. However, the following years saw 6.27% revenue change in 2021, 5.95% in 2022, and a projected 8.57% for 2023 and 6.34% for 2024.
For perspective on how the business intelligence market compares to the general software market, global spending on enterprise software was $856 billion in 2022.
2. The total enterprise data volume reached 2,025 terabytes by the end of 2022 (Source)
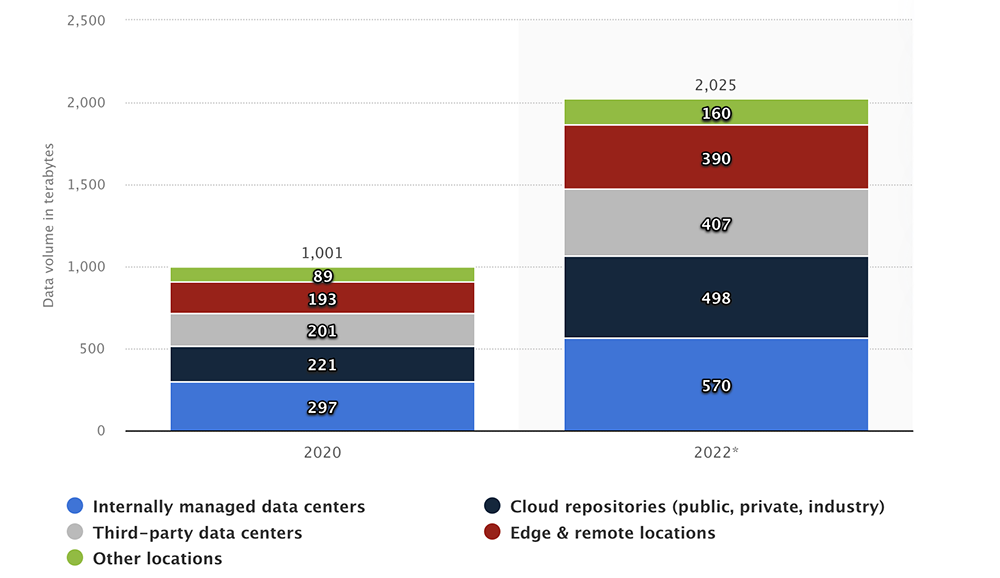
This increase to 2,025 terabytes (TB) was a 42.2% average annual growth from a total volume of 1,001 TB in 2020. The majority of this data is stored in internally managed data centers (570 TB) and cloud repositories (498 TB). Other locations for data storage are third-party data centers (407 TB), edge and remote locations (390 TB), and other locations (160 TB).
With total data volume doubling in just two years, this points to an exponential increase in data collection moving forward. As more companies opt for business intelligence software, more data will be collected. This will allow enterprises to leverage more informed decision-making regarding their products and business operations.
3. A Gartner study found that 81% of business leaders have used BI and analytics software, with 46% of them adopting it in the last 2 years
(Source)

According to survey responses, small and midsize businesses (SMBs) are adopting business intelligence and analytics software at the same rate as enterprises. This shows that businesses of all sizes are finding useful applications for BI solutions.
Of the companies surveyed, an equal number of respondents said they prioritize user experience and training and support services when looking to buy BI and data analytics software, at 84%. Nearly as many (83%) said they prioritize data privacy and reporting capabilities.
Also equally key were scalability and seamless integrations, at 82%. Further, 81% of respondents valued cybersecurity and a distributed cloud network.
Rounding out the responses were automation, AI, and machine learning at 79%, and the option to unbundle features for tailored pricing at 74%.
4. The Gartner study also found that the countries with the highest adoption are Italy and Colombia at 60%, Spain at 56%, and Portugal and Brazil at 54%
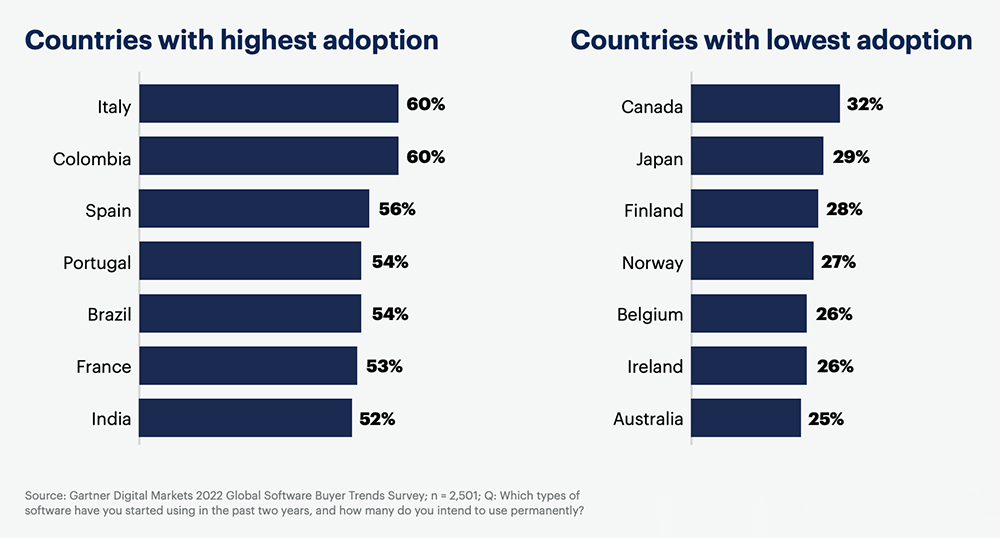
Rounding out the top of the list are France with 53% and India with 52% investing heavily in BI and analytics solutions.
Conversely, countries with the lowest adoption are Australia at 25%, Ireland and Belgium at 26%, Norway at 27%, Finland at 28%, Japan at 29%, and Canada at 32%.
That said, for the countries with lower adoption rates it doesn’t necessarily mean the firms there have never used business intelligence software. These percentages include firms that may have used BI software but haven’t done so in the last two years.
This may be due to budget cuts, choices made by the decision-makers, or other reasons.
Regardless, data suggests the adoption rate of BI software is generally higher in developing economies as opposed to developed economies.
5. The marketing and PR industry has had the highest adoption rate (61%) for BI and data analytics software over the past two years
(Source)
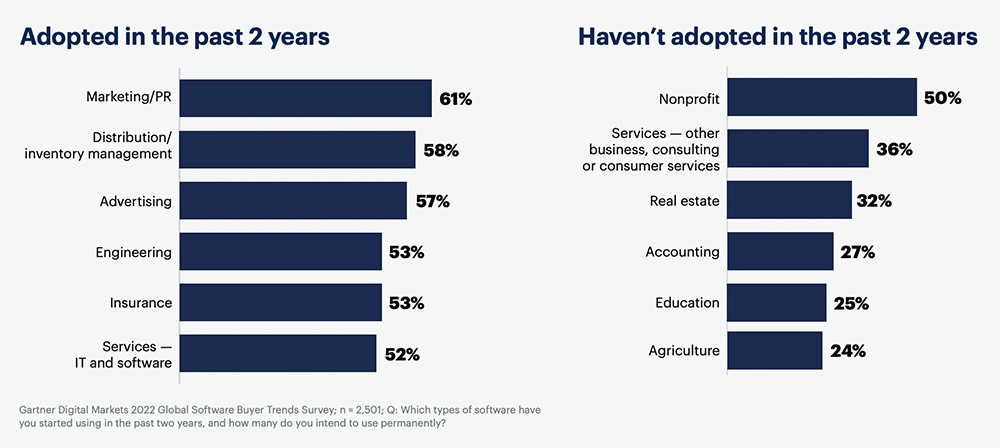
Among the 26 industries Gartner surveyed, the distribution and inventory management industry had the second-highest adoption rate at 58%. Advertising was third with 57%, engineering and insurance had an adoption rate of 53%, and IT and software services were at 52%.
Furthermore, the study found that 50% of all nonprofits hadn’t adopted BI software in the last two years. The same was true for 36% of other business, consulting, or consumer services, 32% of real estate companies, 27% of accounting firms, 25% of educational institutions, and 24% of agricultural organizations.
This is why business intelligence and data analytics software companies target buyers from high-adoption industries like the marketing and PR industry. However, demand generation strategies can bring lower-adoption industries like nonprofit organizations into the fold.
6. 92% of product decision-makers believe data and analytics are critical to business success (Source)
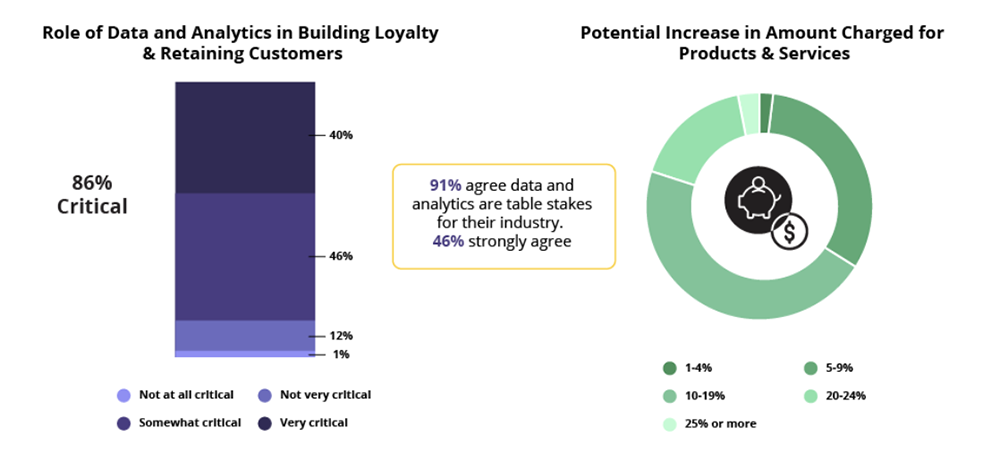
To take it a step further, 41% of the decision-makers surveyed by Sisense say data and analytics are “very critical” to the success of their business. Also, roughly four out of five, or 86%, believe providing data and analytics for customers is critical for building loyalty and retaining customers.
The survey found that 46% of respondents believe data and analytics are at least “somewhat critical” to building customer loyalty while 12% say data and analytics are “not very critical” to this goal.
Further, only 1% of respondents say data and analytics are not at all critical to building customer loyalty. The near unanimous response to the contrary indicate that business intelligence and data analytics play a role in organizational success.
Meanwhile, three out of four respondents believe that all of their customers need better data and analytics, while all business leaders who responded to the survey believe that at least some of their customers do.
Respondents said data analytics allows for a potential increase in prices for products and services. Nearly one in four of those surveyed believe they can increase prices by 20% or more, with some saying 25% or more.
7. Organizations draw from an average of 400 data sources to feed their business intelligence and analytics systems (Source)
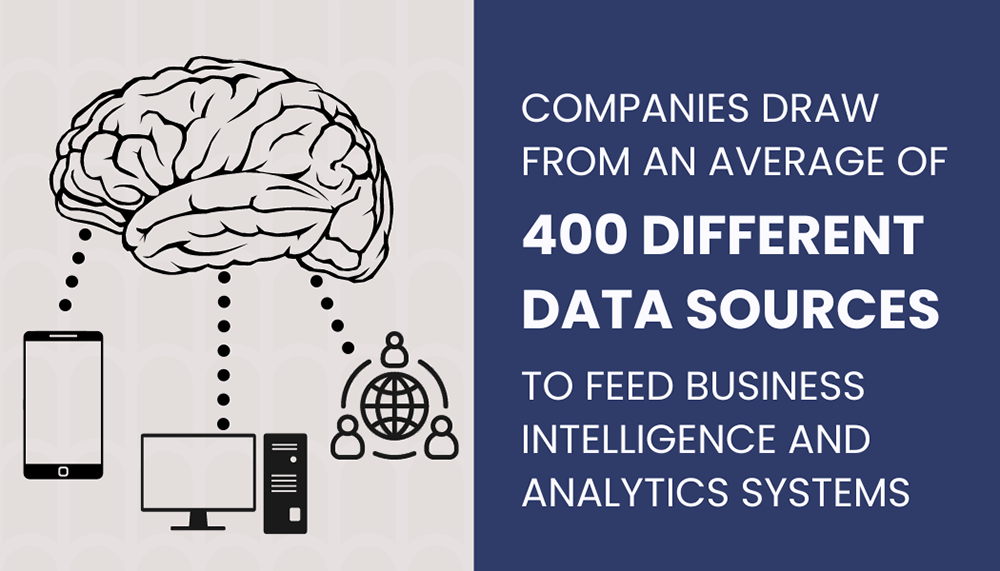
The survey by Matillion and IDG Research found that for 20% of organizations, the number of data sources harnessed for BI and data analysis systems increases to 1,000. These sources include smartphones, computers, social media networks, websites, e-commerce platforms, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
The survey also found that data volumes are growing at an average of 63% per month within organizations. Roughly 10% respondents said their data volumes were increasing at 100% or more per month — meaning the amount of data they’re storing doubles each month.
Furthermore, the data professionals who responded to the survey said 37% of their organizational data is held in cloud data warehouses. An additional 35% of their data is stored in on-premises data warehouses, and one-fourth is stored in off-site and non-cloud data warehouses.
Typically, respondents said high-access data is kept in cloud and in-house data warehouses for easy and quick access. Meanwhile, legacy records and data that aren’t regularly accessed are often stored in non-cloud, off-site data warehouses.
That said, 99% of respondents said they will migrate completely to cloud data warehouses over the next two years.
8. The most popular media for analytics are reports and dashboards, used by 97% and 96% of organizations, respectively (Source)
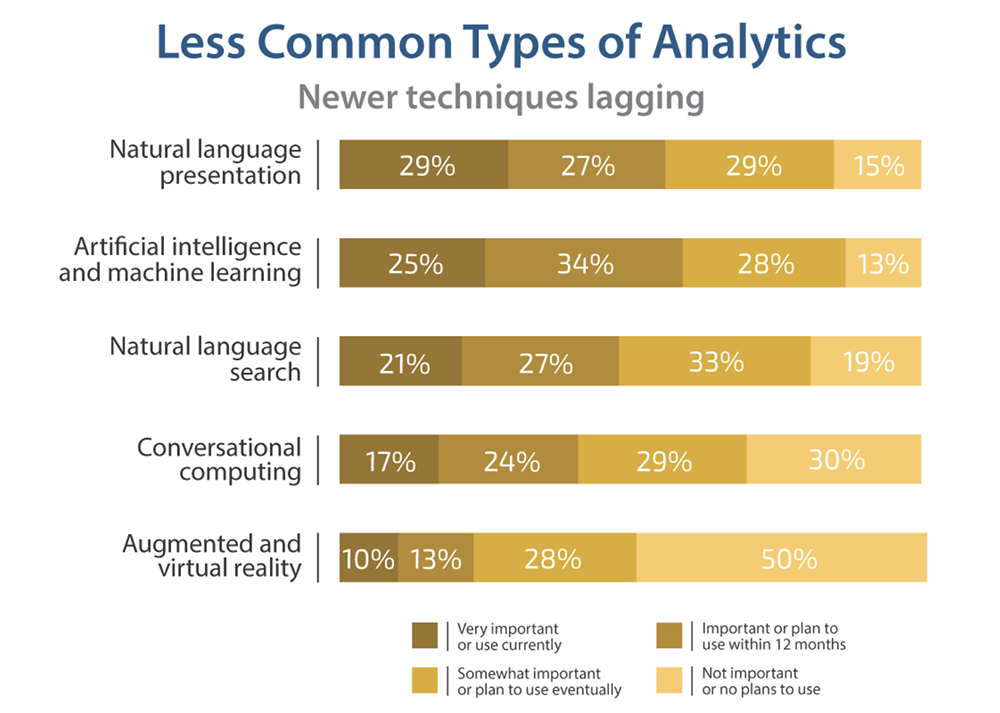
While reports and dashboards are popular, newer techniques like natural language presentation, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are lagging.
Of those surveyed, only 29% of respondents consider natural language presentation to be very important or use it currently, and 15% have no plans to use it. Meanwhile, only 25% of respondents use artificial intelligence and machine learning, and 13% do not intend to use it in the future.
Other less common types of analytics include natural language search, conversational computing, and augmented and virtual reality.
However, more than eight in 10 respondents say they eventually plan to use natural language processing (natural language presentation and natural language search) and artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Natural language processing will help make analytics more accessible to users across the board. Furthermore, proper use of AI and machine learning will help increase the value of business analytics while allowing complex analyses to be completed in a fraction of the time.
That being said, the adoption rates for business intelligence and data analytics software that offer these less common types of analytics are generally lower, especially because of higher prices.
9. In roughly 73% of businesses, 50% or less of their workforce use analytics (Source)
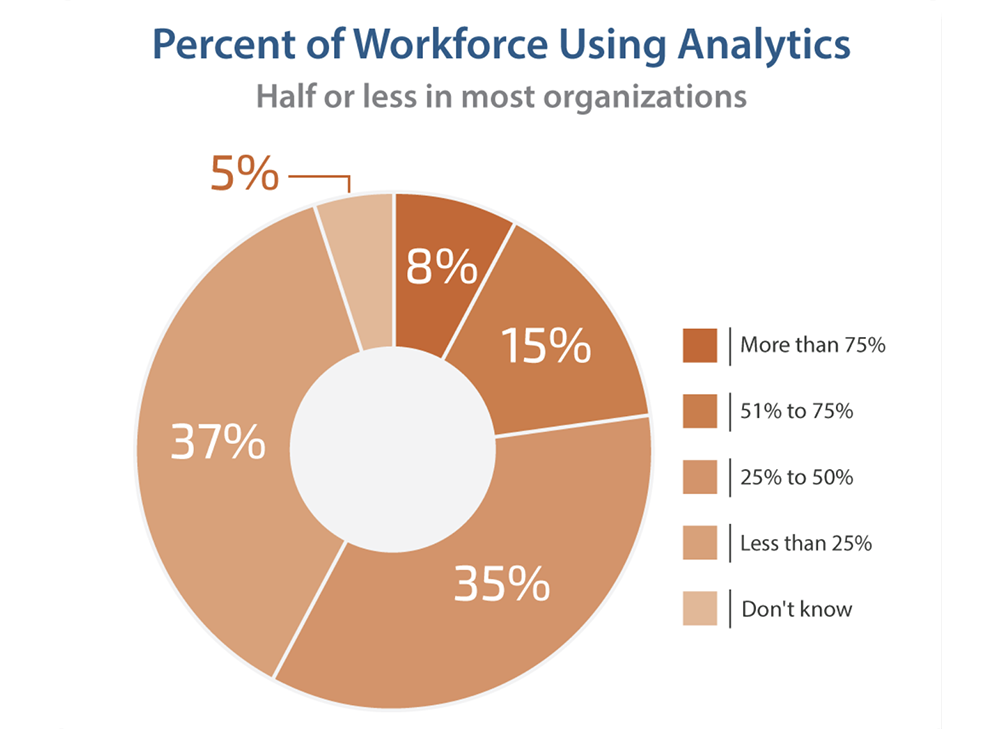
Only 8% of the organizations surveyed by Ventana Research Analytics reported that more than 75% of their workforce utilize analytics.
Meanwhile, only 15% of businesses say 51% to 75% of their workers utilize analytics.
In approximately 37% of organizations, 25% to 50% of the workforce uses analytics, and in 35% of companies it’s used by less than 25%. Of respondents, 5% said they didn’t know how much of their workforce leverages analytics.
While not every employee in a business needs to use analytics, certain departments should have a 100% adoption rate, such as marketing and PR.
10. One in four organizations use 10 or more business intelligence platforms (Source)
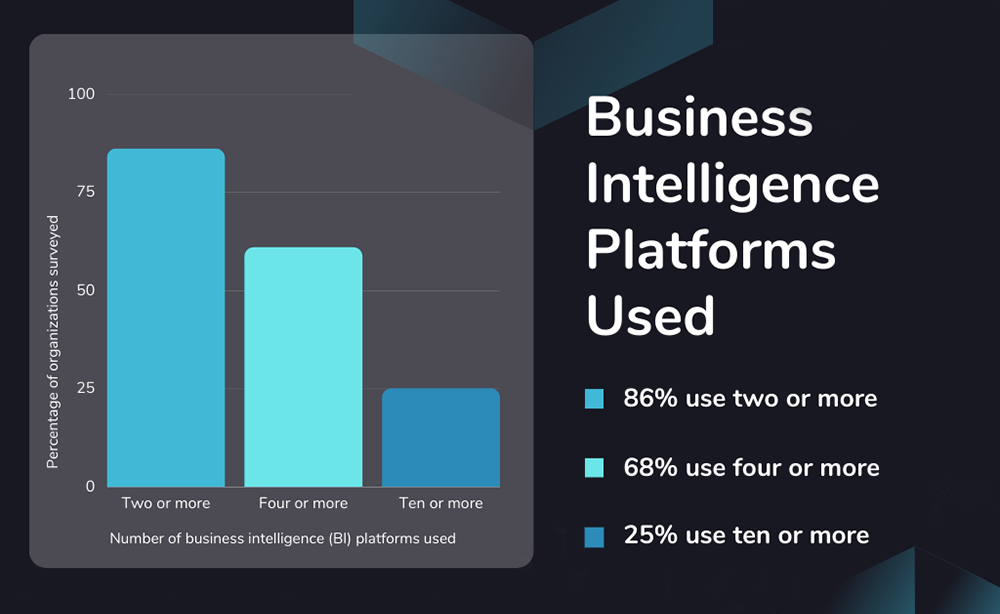
Meanwhile, the informal social media survey by Boris Evelson at Forrester Research found that 68% of organizations said they use four or more business intelligence platforms. The largest section of respondents, at 86%, report using two or more BI platforms, and 25% use 10 more more.
While it was an informal social media survey, it indicates that a strong majority of businesses utilize at least two BI software solutions. Here are some possible reasons:
- Companies may use different BI software in different departments. For example, BI software that specializes in marketing and PR analytics would be used in that department.
- Organizations may use different BI software at different levels. For example, they may use one software for customer success but another with tighter security to manage high-profile customers.
- When a company needs a new feature, such as AI and machine learning, typically they will find a new BI software that offers it rather than transferring their whole ecosystem to the new software.
11. 79% of organizations plan to increase their cloud data management in the next 12 months
(Source)
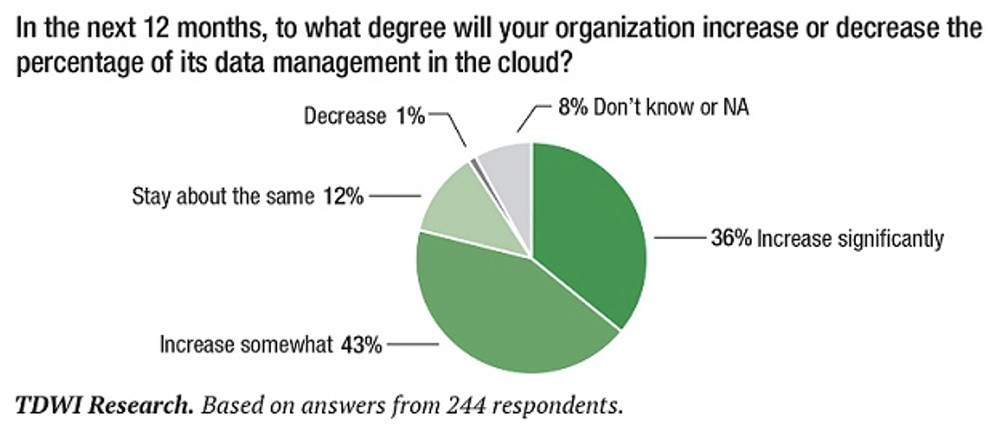
The survey of data integration trends by TWDI Research found that 36% of organizations plan to “increase significantly” their cloud data management over the next year. Meanwhile, 43% of respondents said they plan to “increase somewhat” during that same timeframe, for a total of 79% of organizations intending to scale up their cloud data management.
An additional 12% said they intend to keep it about the same while 1% plan to decrease the percentage data they store on the cloud.
Cloud migration may be as important as analytics in across-the-board data integration and convenient data access. On the other hand, some organizations prefer to keep analytics on-premises because data sets and models are company assets that need to remain absolutely secure — and they believe keeping such assets on the premises is the best way to ensure their safety.
That being said, four out of five of respondents surveyed said they have a cloud data warehouse, and it’s reasonable to expect that number to increase.
12. Notion has the largest business intelligence software market share with 19.29% and 91,909 customers (Source)
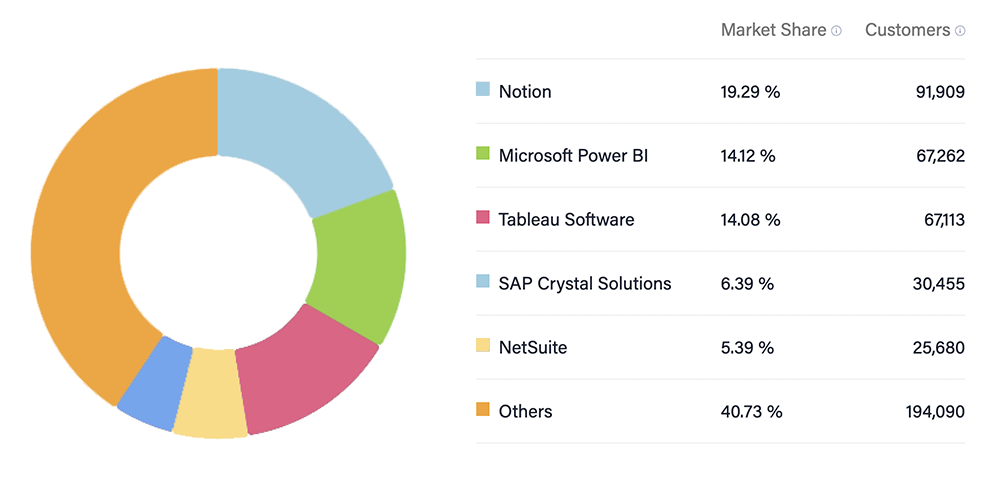
Microsoft Power BI has the second largest share in the global business intelligence market with 14.12% and 67,262 customers. It recently pulled ahead of Seattle-based company Tableau Software, which has a share of 14.08% and 67,113 customers.
SAP Crystal Solutions comes in fourth place with a 6.39% market share and 30,455 customers. NetSuite is in fifth place with a 5.39% market share and 25,680 customers. Other solutions represent 40.73% of the market share with a total of 194,090 customers.
Other key players in the BI software industry include SAP Business Objects, Cognos, HeapAnalytics, QlikView, Alexa, and SAP Analytics Cloud.
Of the companies that use BI software, 82,456 have between 20-49 employees, 60,523 have 100-249 employees, and 73,691 have nine or fewer employees.
13. The US has the most companies using business intelligence software, accounting for 61.88% of all users (Source)
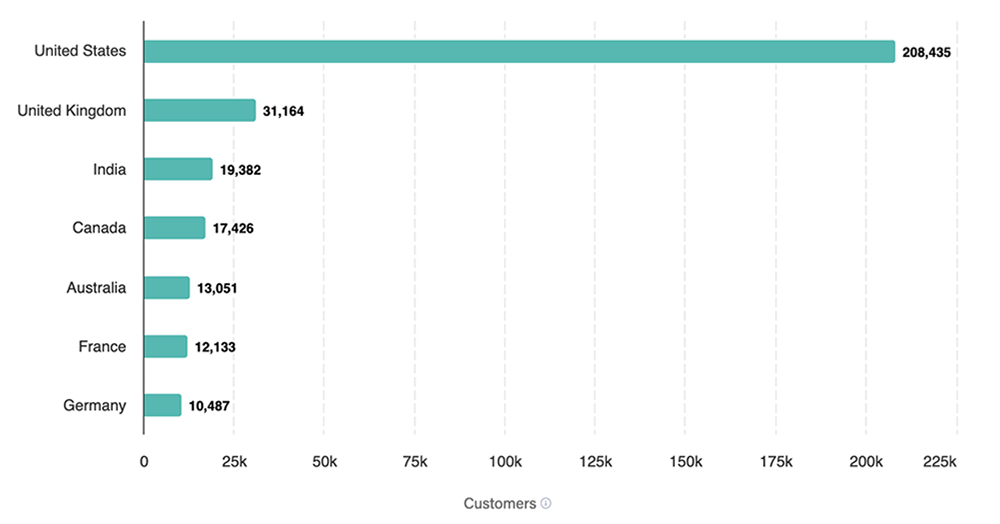
The US’s share of companies using business intelligence tools totals 208,435. Meanwhile, the United Kingdom comes in second with 9.25% of users (31,164 companies) and India is in third place, accounting for 5.75% of all users (19,382 companies).
Despite so many customers being in the US, the country doesn’t have the highest adoption rate for BI software. In the future, we’ll likely see a lot of developing countries, like India, dominating the chart.
What Business Intelligence Statistics and Trends Indicate About the Future
Business success has always hinged on leveraging customer data. Today’s business intelligence and data analytics software collect, analyze, and provide information on almost everything, making it a necessity for businesses. They provide real-time, interactive data visualization and actionable insights for increasing profitability, successfully implementing initiatives, and making business decisions.
Over the last decade, the adoption of BI software has been rapidly increasing, especially in the last two years. It’s reasonable to expect a similar growth curve moving forward.
Furthermore, these business intelligence statistics indicate that while developed economies dominate the market today, the future of Big Data will see developing countries represent a large percentage of future market growth.
We will also likely see significant expansion in business intelligence software that incorporates new AI-powered technologies.



